
Back جغرافيا إسكتلندا Arabic স্কটল্যান্ডের ভূগোল Bengali/Bangla Geografía de Escocia Spanish Eskoziako geografia Basque Skotlannin maantiede Finnish Géographie de l'Écosse French Cruinn-eòlas na h-Alba Scots/Gaelic Xeografía de Escocia Galician Škotijos geografija Lithuanian Географија на Шкотска Macedonian
 | |
 | |
| Continent | Europe |
|---|---|
| Region | British Isles |
| Area | |
| • Total | 80,231 km2 (30,977 sq mi) |
| • Land | 97% |
| • Water | 3% |
| Coastline | 11,796 km (7,330 mi) |
| Borders | England 154 km (96 mi) |
| Highest point | Ben Nevis 1,346 m (4,416 ft) |
| Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean, 0 m |
| Longest river | River Tay 188 km (117 mi) |
| Largest lake | Loch Lomond 71.3 km2 (27.5 sq mi) |
| Climate | Temperate, Subarctic, Tundra |
| Terrain | mountains, hills, forest, bog, urban |
| Natural resources | iron, zinc, potash, silica sand, coal, fish, timber, wildlife, petroleum, natural gas, hydropower |
| Natural hazards | windstorms, floods |
| Environmental issues | climate change, renewable energy, waste disposal and water pollution |
| References | |
| [1][2] | |
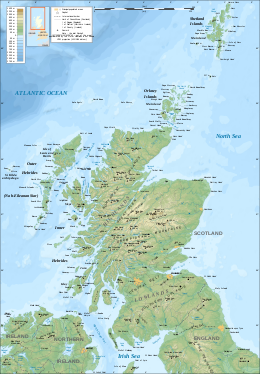
The geography of Scotland is varied, from rural lowlands to unspoilt uplands, and from large cities to sparsely inhabited islands. Located in Northern Europe, Scotland comprises the northern part of the island of Great Britain as well as 790 surrounding islands encompassing the major archipelagos of the Shetland Islands, Orkney Islands and the Inner and Outer Hebrides.[3] The only land border is with England, which runs for 96 miles (154 kilometres) in a northeasterly direction from the Solway Firth in the west to the North Sea on the east coast.[4] Separated by the North Channel, the island of Ireland lies 13 nautical miles (24 kilometres) from Mull of Kintyre on the Scottish mainland.[5] Norway is located 190 nmi (350 km) northeast of Scotland across the North Sea. The Atlantic Ocean, which fringes the coastline of western and northern Scotland and its islands, influences the temperate, maritime climate of the country.[6]
Scotland contains the majority of mountainous terrain in the UK. The topography of Scotland is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault which traverses the Scottish mainland from Helensburgh to Stonehaven.[7] The faultline separates two distinctively different physiographic regions; namely the Highlands to the north and west and the Lowlands to the south and east.[8] The more rugged Highland region contains the majority of Scotland's mountainous terrain, including the highest peak, Ben Nevis.
Lowland areas, in the southern part of Scotland, are flatter and home to most of the population, especially the narrow waist of land between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth known as the Central Belt.[8] Glasgow is the largest city in Scotland, although Edinburgh is the capital and political centre of the country.[9] While the Lowlands are less elevated, upland and mountainous terrain is located across the Southern Uplands.
An abundance of natural resources such as coal, iron and zinc contributed significantly to the industrial growth of Scotland during the 19th and early 20th centuries.[10] Today, energy is a major component of Scotland's economy.[11] Whilst Scotland is a large producer of petroleum, the production potential of renewable energy has emerged as an important economic and environmental issue in recent years.[12]
- ^ "Standard Area Measurements (Latest) for Administrative Areas in the United Kingdom". Open Geography Portal. Office for National Statistics. 24 April 2024. Retrieved 6 May 2024.
- ^ "A Beginners Guide to UK Geography (2023)". Open Geography Portal. Office for National Statistics. 24 August 2023. Retrieved 9 December 2023.
- ^ "Scotland". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 16 August 2007.
- ^ Munro, D (1999). Scotland Atlas and Gazetteer. Harper Collins. pp. 1–2.
- ^ "North Channel", Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- ^ "Scottish climate". Met Office. 2001. Archived from the original on 27 May 2007. Retrieved 20 August 2007.
- ^ "Overview of Highland Boundary Fault". Gazetteer for Scotland, University of Edinburgh. Retrieved 23 August 2007.
- ^ a b "Loch Lomond to Stirling – the Highland Line". Scottish Natural Heritage (SNH). Archived from the original on 17 February 2013. Retrieved 23 August 2007.
- ^ "Mid 2004 Localities estimates – Localities in descending order of size" (PDF). General Register of Scotland (GROS). 2004. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 23 August 2007.
- ^ Lynch, M (2001), Industry to 1770s; pp211 Oxford Companion to Scottish History
- ^ Shepherd, Mike (2015). Oil Strike North Sea: A first-hand history of North Sea oil. Luath Press.
- ^ "A vision for the future of energy in Scotland". Speech by the Minister for Enterprise, Energy and Tourism, Jim Mather. Scottish Executive. 23 May 2007. Retrieved 24 August 2007.[permanent dead link]
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search